Lymphatic Drainage
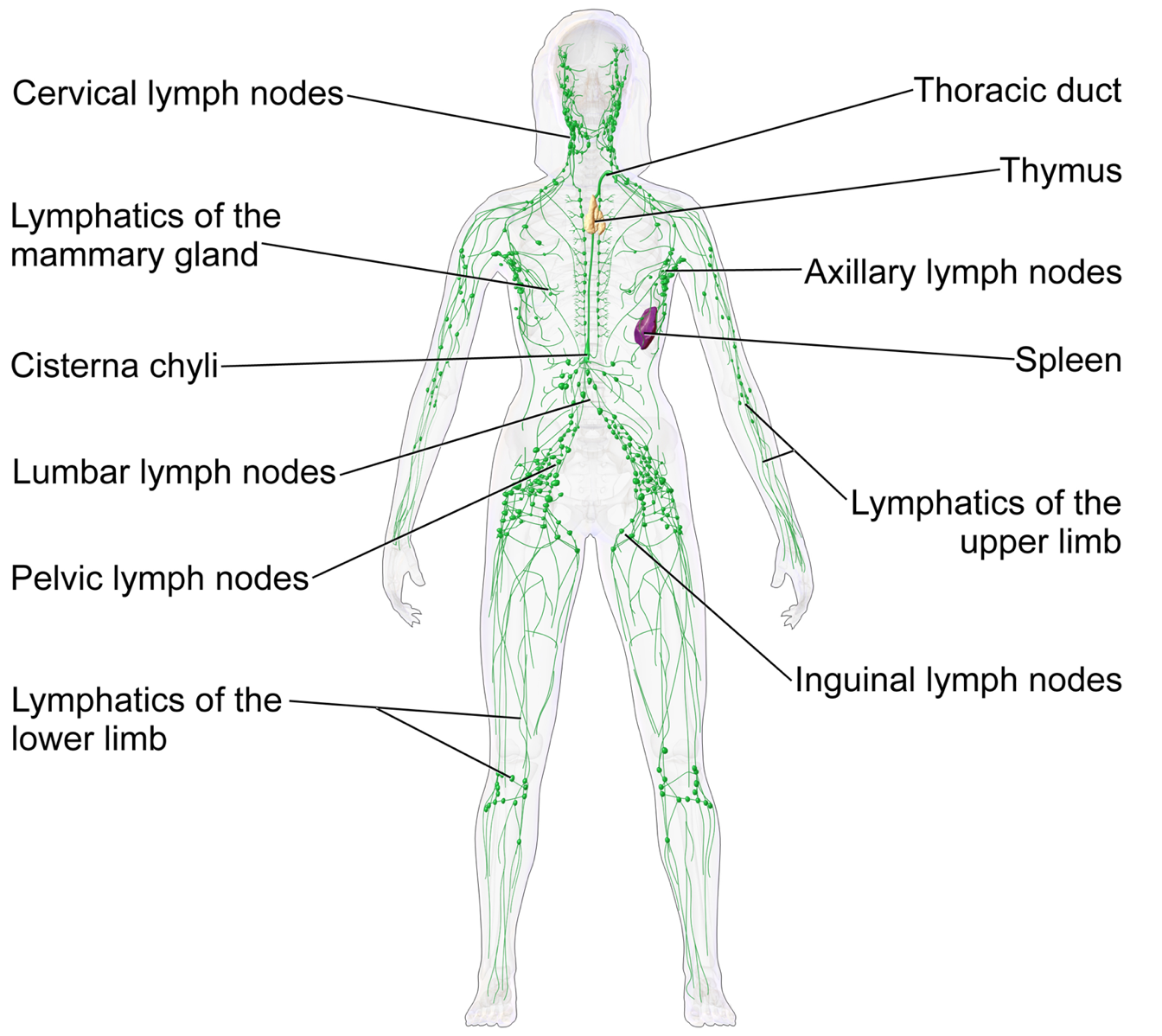
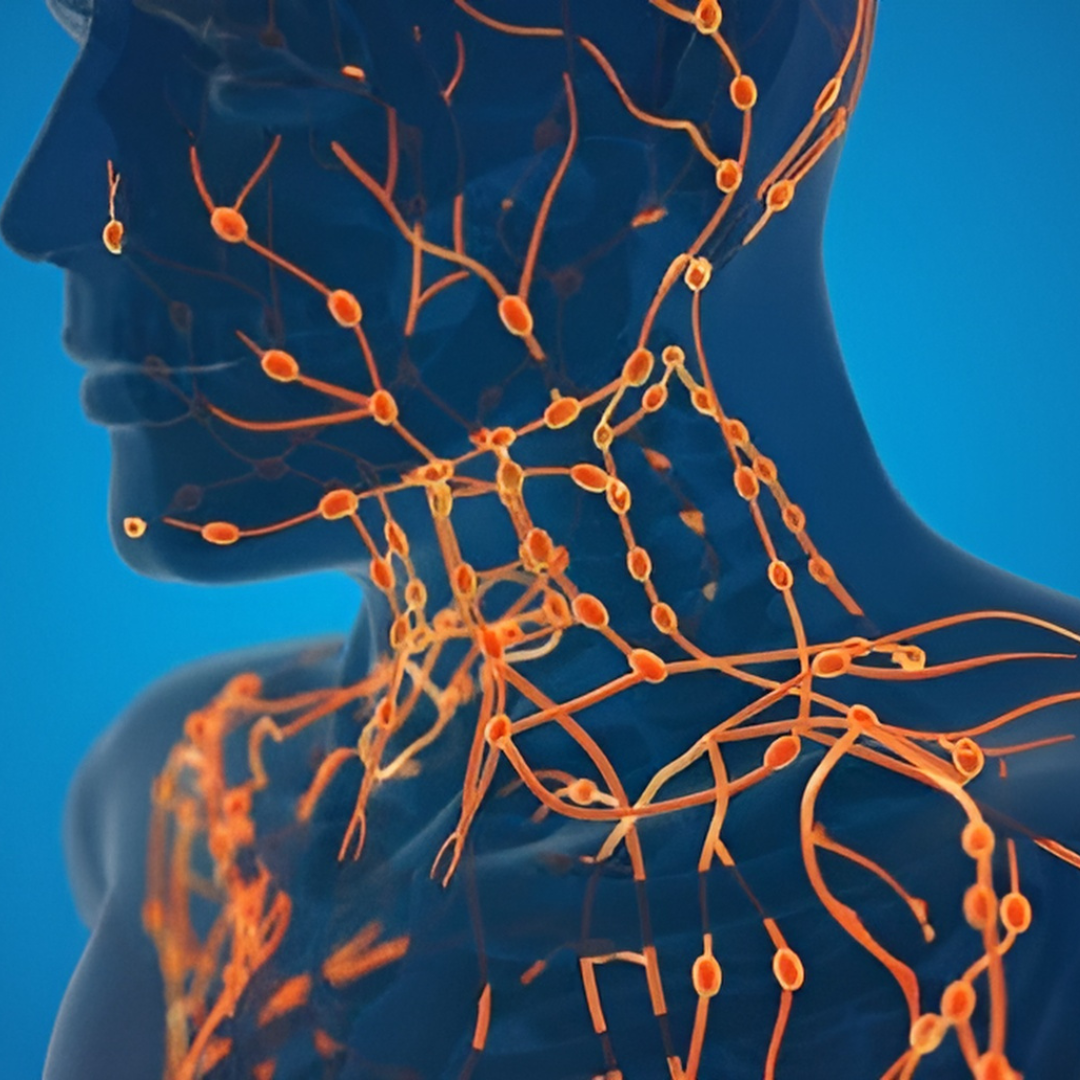
Lymphatic drainage is the natural function performed by your lymphatic system. As blood flows throughout your body, blood plasma leaks into the interstitium, which is the space between cells. This thin, yellowish interstitial fluid is called lymph. It is a multicomponent mixture of water, nutrients and proteins, lymphocytes, and all the substances your cells produce and excrete. As your muscles contract, lymph is squeezed into lymphatic capillaries and then into larger lymphatic vessels. These drain into lymph nodes all over your body. The largest nodes are in the neck, groin, and armpits. The lymph nodes filter out harmful substances, and the purified lymph flows into the lymph ducts. From here, it is returned to your bloodstream.
Lymphatic drainage problems can occur for a wide variety of reasons, including genetic, lymph node removal or cancer, chronic infections and inflammation, poor nutrition, lack of movement, surgical procedures, and more. If lymph doesn’t drain properly, your lymphatic system may become congested and inflamed. This can cause painful swelling known as lymphedema.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage
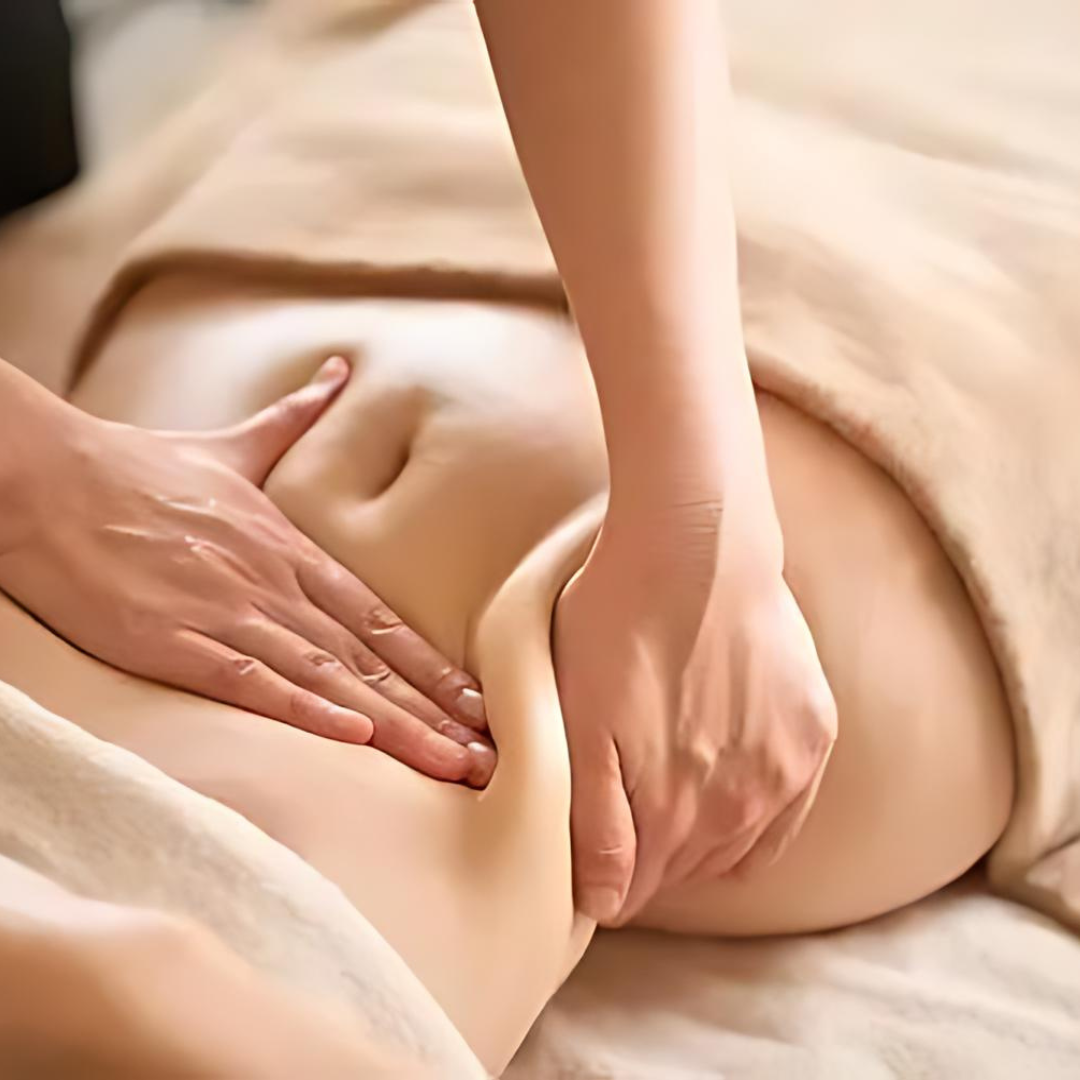
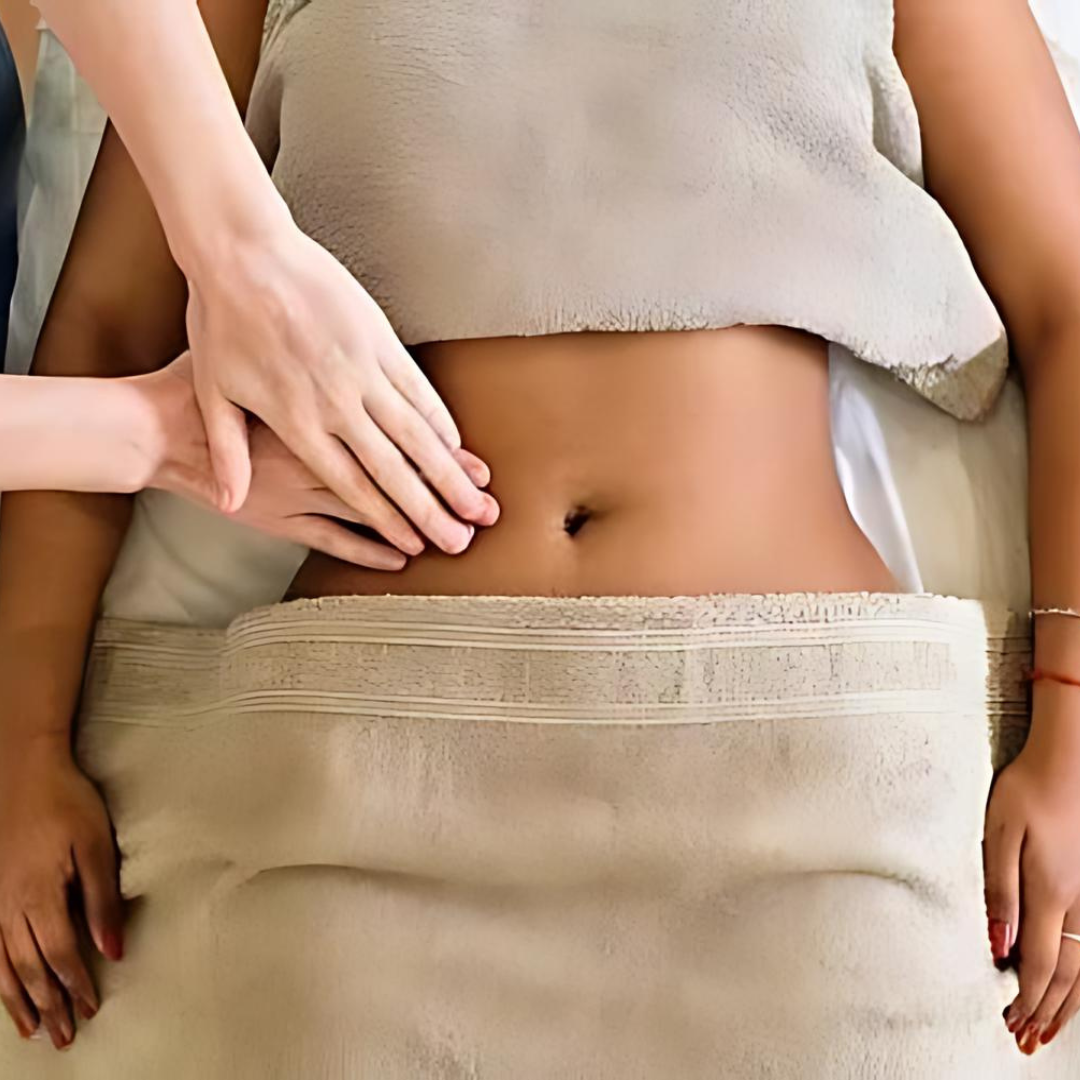
This gentle massage technique moves lymph out of an affected area and stimulates lymph nodes. The therapist applies light pressure to stretch the skin and boost lymph flow in the correct direction. This specialized and deeply relaxing massage technique aims to help the body maintain proper blood circulation, body fluid balance, and immune functions.Â
What Does the Lymphatic System Do?
The lymphatic system eliminates waste and protects your body from disease. It has five major functions:Â
- Draining excess fluid from all your body tissues.
- Absorbing fats, water-soluble vitamins, and proteins from your digestive system and carrying them to the bloodstream.
- Releasing white blood cells to fight diseases and infections.
- Filtering toxins out of your body fluids.
- Transporting waste products and damaged cells away from the tissues.
What Are the Symptoms of Poor Lymphatic Drainage?
- Fluid retention can cause swelling and pain in the arms, legs, fingers, toes, head, or neck.
- The affected area may have aches and pains or a feeling of heaviness.
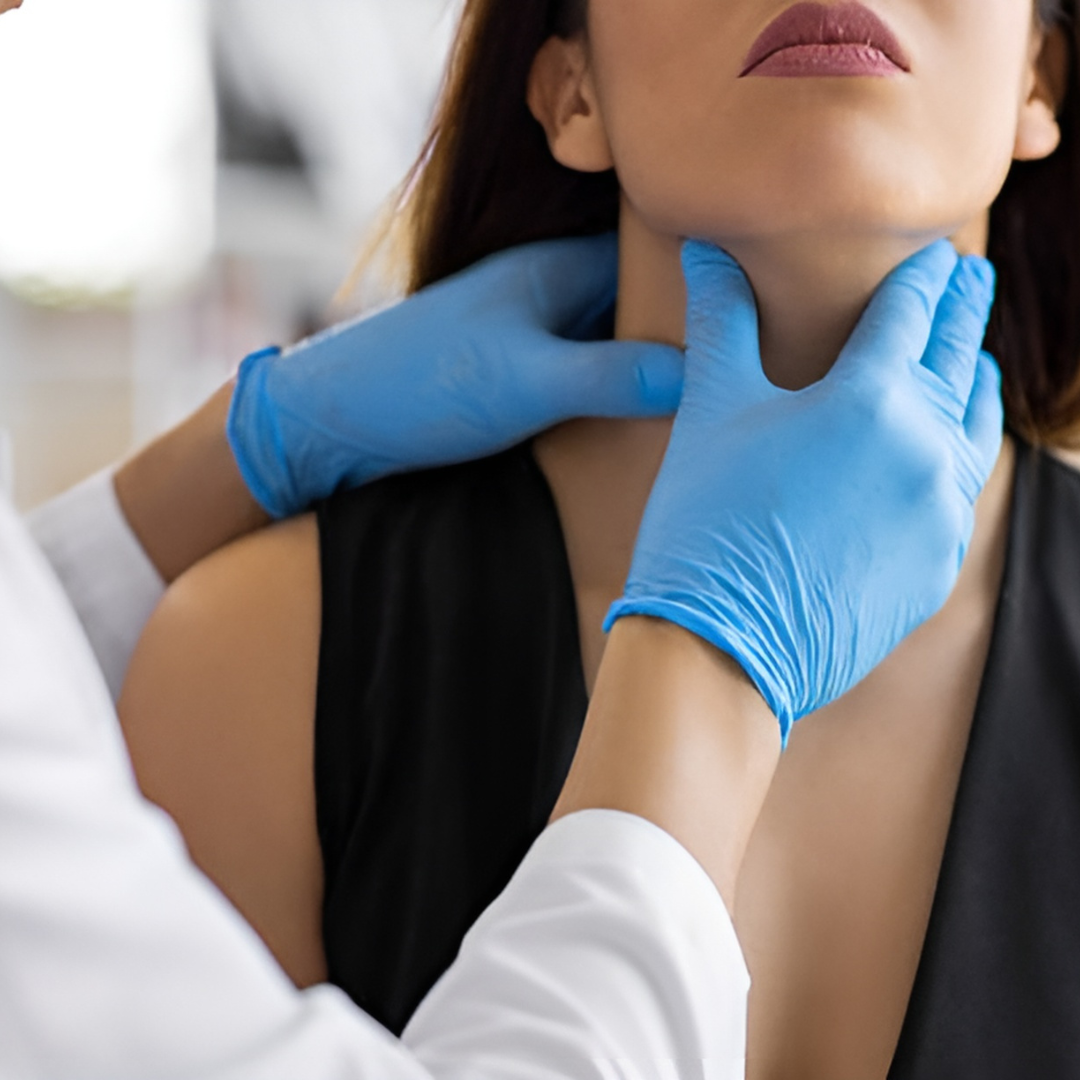
- Swollen lymph nodes that do not go down.
- You may notice skin problems such as discoloration, blisters, infection, or fluid leaking.
- It can cause earache, vision problems, or nasal congestion.
- You may have difficulty breathing, swallowing, or talking.
How Does Lymphatic Drainage Therapy Work?
Lymphatic Drainage Therapy works by redirecting lymph to functional parts of the lymphatic system. This great therapy stimulates the contraction of lymphatic vessels and helps decongest the affected area. It is mild, non-invasive, and will bring you relief and improved functionality.
Lymphatic Drainage Therapy can
- Alleviate edema and lymphedema, and other inflammatory conditions.
- Enhance the function of the lymphatic system
- Boost immunity.
- Provide relief from chronic pain.
- Combat fatigue and restore energy.
- Improve the function of joints.
- Decrease the time for postoperative healing.
- Reduce swelling.
- Soften scars and fibrotic tissue.
- Invigorate your sense of well-being.
Office Hours
Find Out When We Are Open